Research
Publications
———————————————————————————————————
Journal Publications
J4 Kazi Ahmed Asif Fuad, Shahriyar Masud Rizvi, “Varying Sample-Width to Realize Area-Efficient FPGA Realization of Sobel-Fieldman Edge Detector”, AIUB Journal of Science and Engineering (AJSE) Vol. 14, No. 1, August 2015 (ISSN: 1608-3679).
J3 Kazi Ahmed Asif Fuad, Shahriyar Masud Rizvi, “Hardware Software Co-Simulation of Canny Edge Detection Algorithm” International Journal of Computer Applications 122(19): 7-12, July 2015.
J2 Kazi Ahmed Asif Fuad, Shahriyar Masud Rizvi, “Hardware/Software Co-Simulation of Gradient-based Edge Detectors: A Comparative Study”, STM Journal of Image Processing and Pattern Recognition Progress (JoIPPRP), Vol. 2, No. 3, September, 2015 (ISSN: 2394-1995).
[J1] Md. Maruf Ibne Hasan, Kazi Ahmed Asif Fuad, Nipu Rani Barai, Maroof Muhammad Hasan, Shahriyar Masud Rizvi, “FPGA and Microcontroller based Data Acquisition System using Two Wire Serial Communication” Journal of Embedded System and Applications, Vol. 2, No. 3, July 2014.
Conference Publications
C4 Kazi Ahmed Asif Fuad, Pierre-Etienne Martin, Romain Giot, Romain Bourqui, Jenny Benois-Pineau, Akka Zemmari (2020) Features Understanding in 3D CNNs for Actions Recognition in Video. International Conference on Image Processing Theory, Tools and Applications (IPTA) 2020, Paris, France [Accepted].
C3 Mahamud M.S., Islam M., Shila A.S., Asif Fuad K.A., Islam M.R. (2019) Watch IT Version-II: An Assistive Device for Hearing and Speaking Impaired. In: Arai K., Kapoor S., Bhatia R. (eds) Intelligent Systems and Applications. IntelliSys 2018. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 869. Springer, Cham.
C2 Tasneem Sanjana, Kazi Ahmed Asif Fuad, Mehrab Masayeed Habib, Ahmed Amin Rumel, “Automated anti-collision system for automobiles” 2017 International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Communication Engineering (ECCE), Cox’s Bazar, 2017, pp. 866-870.
C1 Kazi Ahmed Asif Fuad, Md. Maruf Ibne Hasan, Laila Nawsheen Manzoor, Mohammad Abdul Mannan, Chowdhury Akram Hossain, “Design and simulation of centralized load controlled automated power system network (CLCAPSN)” 2015 IEEE International WIE Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering (WIECON-ECE), Dhaka, 2015, pp. 61-64.
Projects
———————————————————————————————————
IPCV Master Thesis: Recognition of Sports Gestures with 3D Deep CNNs: Explanation of Networks
Supervised by: Professor Jenny Benois-Pineau.
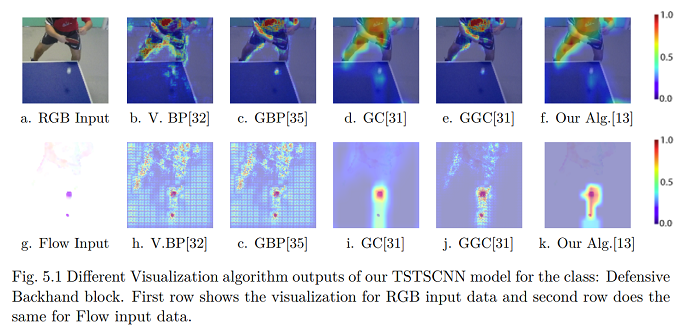
Abstract: Human Action Recognition is one of the key tasks in video understanding. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) are often used to tackle this issue. Although they usually perform impressively for such action classification tasks, their interpretability remains challenging. During the last decade, various analytical visualization techniques such as Vanilla gradient-based Backpropagation or Grad-CAM help understanding features, from input space, that strongly supports the final decision and further network optimization.
In this thesis, we propose a novel visual features understanding technique for 3DCNNs for action recognition. Its objective is to find salient features that played a key role in decision making of the network. Our proposed visualization technique takes the features from the last Convolutional layer before the fully connected layers of a trained model and generates a binary feature importance map per channel. To reduce the contribution of relatively low magnitude features, the final importance map is generated as a weighted sum of all binary channel maps. Finally, the resulting importance map is propagated to the original frame thus “explaining” the regions in them that contribute to the final decision. The method is fast and does not require gradient computation.
Our proposed technique is applied to the Twin Spatio-Temporal Convolutional Neural Network (TSTCNN) we designed for Table Tennis Action recognition task that was trained on our dataset TTStroke-21. Feature visualization is performed at the RGB and Optical flow branches of thenetwork. Obtained results are compared to other visualization techniques both in terms of human understanding and similarity metrics between importance maps generated by different methods: Vanilla gradient–based Backpropagation, Guided Backpropagation and Grad-CAM. The metrics show that generated maps are similar to those obtained with known Grad-CAM method, e.g. Pearson Correlation Coefficient between the maps generated of RGB data for Grad-Cam and our method is 0.7 ± 0.05 and 0.72 ± 0.06 on Optical Flow data. Visualization methods have been applied to RGB Spatio-Temporal Convolutional Neural Network (RGBSTCNN) and Optical Flow Spatio-Temporal Convolutional Neural Network (OFTSTCNN) to observe whether models with similar architecture trained on the same dataset learn similar kind of knowledge. Comparing all the models, it is observed that Our algorithm is similar to Grad-CAM and Guided GradCAM analytically. Finally, proposed method was applied to existing popular CNN architecture AlexNet and VGG-16 and satisfactory results are obtained. Computationally, the proposed algorithm is twice faster. Hence, this simple computationally inexpensive visualization technique is similar to Grad-CAM but does not require heavy gradient computation.
Master in EEE Thesis: Area-Efficient FPGA realization of Edge Detectors by varying sample-widths and gradient operators and utilizing Software-Hardware Co-Design.
Supervised by: Associate Professor Shahriyar Masud Rizvi.
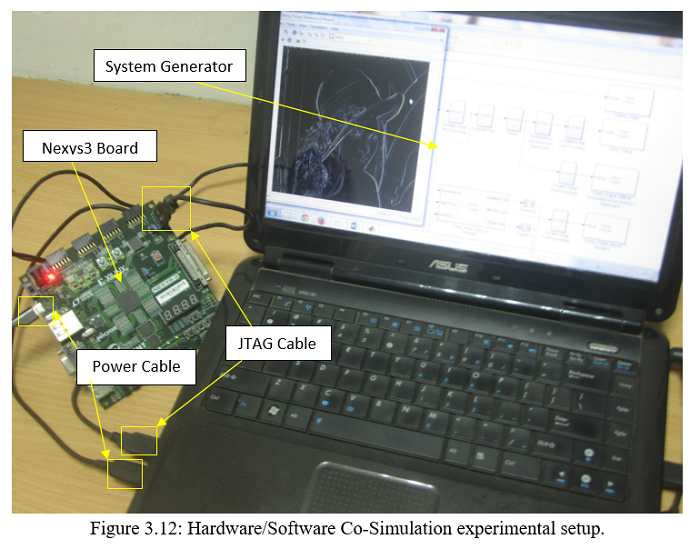
Abstract: This thesis presents a comprehensive comparative study of edge detection techniques and proposes a ovel area-efficient edge detection method for gradient based edge detector such as Sobel-Fieldman algorithm by manipulating input sample widths and, in case of Canny edge detector, manipulating gradient operators. After varying sample-widths we find that some smaller sample widths generate images of a quality that is identical to ones attained from standard sample-width (16:14) but with sufficiently lesser FPGA resources. The sample-width of (6:4) generates images of quality attained in standard sample-size of (16:14) with 27% lesser no of LUTs, 25% lesser no of registers and overall 21% lesser slices. We also varied gradient operators used in Canny edge detection algorithm and found Canny algorithm with Robert operator to be the most area-efficient realization while Canny algorithm with Robinson compass operator is found to be more effective edge detector than traditional Canny edge detector with Sobel-Fieldman operator (the former can detect more edges than any other operator used). All the algorithms were simulated in MATLAB and OpenCV for software realization and later they were realized in hardware Spartan-6 LX16 FPGAs from Xilinx utilizing Simulink (from Mathworks) and System Generator (XSG) (From Xilinx).
Bachelor in EEE Thesis: Design and Implementation of Centralized Load Controlled Automated Power System Network (CLCAPSN)
Supervised by: Ms. Laila Nawsheen Manzoor.
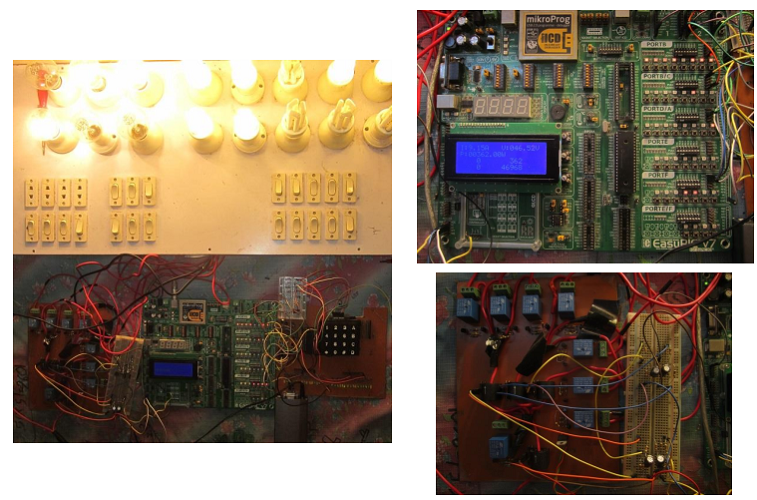

Abstract: We are living in the age where technology is not the major attraction, what level of smart and intelligent the technology is. Power system network is advancing up its way along the smart grid but load end information can make system more efficient. In our project & thesis, we have tried to implement a power system wirelessly connected to the load end side for data transfer about load status. In our project we have tried to bring out the fact “Power Crisis” can be minimized and “Power utilization” can be optimized through monitoring it. To do this we combined embedded system with power circuits. Embedded system has the ability to control a system with high efficiency interfacing the system with digital system as anything interfaced with digital system can be modeled or monitored by “Artificial Intelligence”. User load nature throughout a particular time let the system predict about future and allows the power administrators to design the system and maintain it efficiently. Pre-paid billing makes sure profit alongside making mental awareness not to waste power.
Analysis of Pre-Processing Techniques for Person Re-identification System.
Supervised by Dr. Aurélie Bugeau.
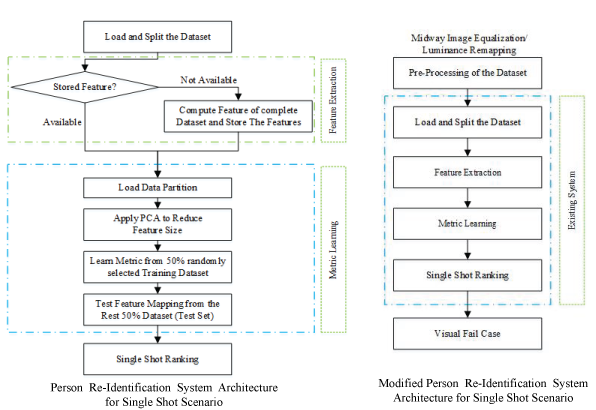
Second part of Tutored Research Development Project of IPCV. For person re-identification use case, we applied two pre-processing techniques: Midway Image Equalization and Luminance Remapping to deal the issues like illumination and viewpoint and around 10% improvement is achieved in the person re-id system by experimented on publicly available Viper dataset.
Multi-Camera Object Detection and Association.
Supervised by Dr. Álvaro García Martín.
First part of Tutored Research Development Project of IPCV. In this project, a State of Art person re-identification in multicamera scenario has been analyzed where many combinations of feature learning, metric learning and ranking algorithms have been implemented. Primarily, we applied Transfer Learning on CNN based feature learning and incorporated score fusion which improved the re-id system by around 5\% to 10\% on different Convolutional Neural Networks.
CERN Openlab Summer Project on “Graph Neural Network (GNN) Inference on FPGAs”.
Supervised by Dr. Sofia Vallecorsa.
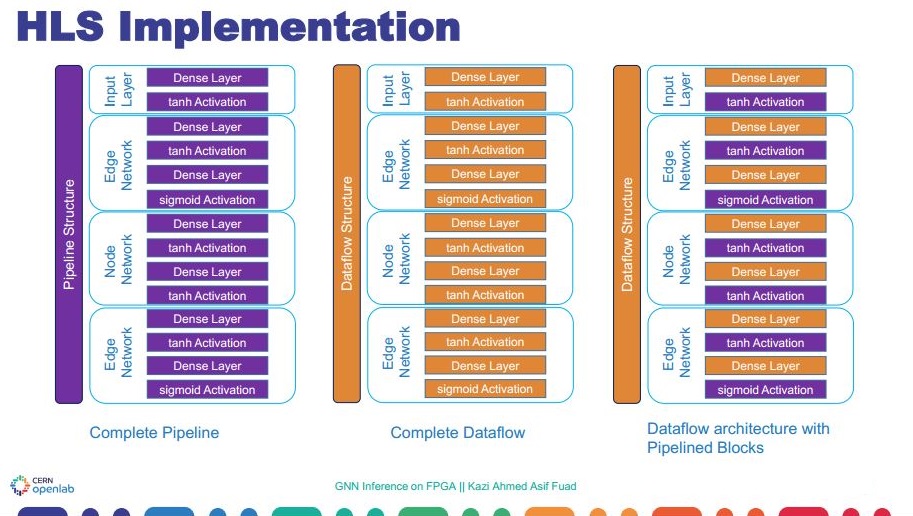
Graph Neural Network possess prospect in track reconstruction for the Large Hadron Collider use-case due to high dimensional and sparse data. In our research, we have used hls4ml, a machine learning inference package for FPGAs that converts a Neural Network model into Synthesis (HLS) C++ code and we have evaluated different architectural approaches: Pipeline, Dataflow and Dataflow with pipeline blocks architectures. Results show that the Pipeline architecture is the fastest but it has some disadvantages such as large loop unrolling and non-functioning reuse factor. On the other hand, our implementation of the system using the Dataflow architecture is too slow but it does not solve large synthesis time. Our proposed modified Dataflow architecture where some of the building blocks are in pipeline architecture shows prominent results compared to Pipeline and Dataflow architecture. Report Code
Deep Learning based Pedestrian Detection.
In this project, YOLO V3 deep-learning object detection technique is fine-tuned for pedestrian detection usecase. This project won 3rd position based on performance over Nine datasets in the People Detection and Biometric Recognition course.
Implementation of Sobel Edge Detector on FPGA with Vivado High Level Synthesis.
Implemented an Sobel filter for Edge Detection in images based on FPGA so that to provides high-speed performance of the algorithm.
Design and Implementation of Pipeline RISC Processor using SystemVerilog.
Implemented a 1-Cycle and 2-Cycle 2 Stage Pipeline RISC Processor capable of executing 5 different type of instructions. It was coded with SystemVerilog HDL and developed using Finite State Machine and Datapath (FSMD) approach with ASM Chart for Spartan-6 LX16 FPGA.
FPGA and Microcontroller based Data Acquisition System using Two Wire Serial Communication.
In this project, Data Acquisition System (DAQ) is implemented that monitors temperature, gas level, humidity and light intensity and sends those information in a wired network to a central controller which displays the information to a computer. The project implements two version of such a DAQ system– one where both the data receiver and controller are implemented in Atmel’s AVR ATmega32 microcontroller and another where the controller is implemented in a Spartan-6 LX16 FPGA from Xilinx (included in Digilent’s Nexys3 FPGA Board) while the data receiver are implemented in the above mentioned micro-controller.
Design and Implementation of an automatic system for Hydrophonic: Fodder usecase.
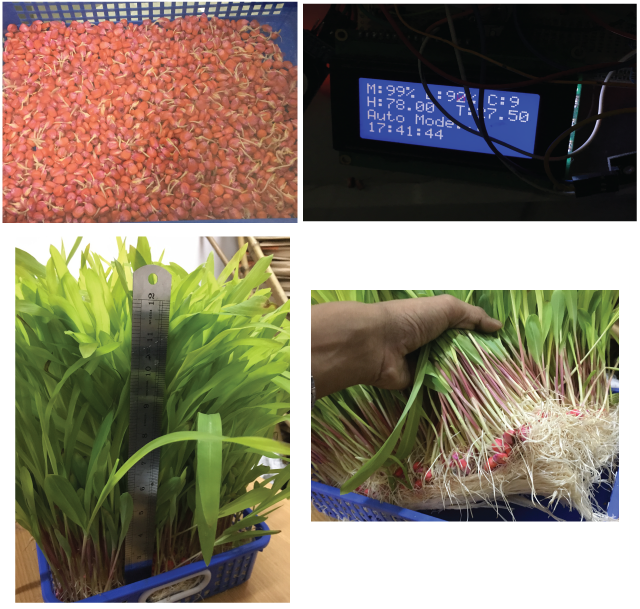

This was an experimental project on Hydrophonic. We successfully produced Fodder from Corn with the implemented automatic irrigation system, equipped with Real Time Clock and sensors. The prototype was developed in Arduino Mega256. Code
Implementation of a Traffic Light Controller (TLC) on Nexys™3 Spartan-6 FPGA Board.
In this project, an automatic Traffic Light Controller with predetermined time sequences for Red, Green and Blue light signals was implemented. The Finite State Machine (FSM) of the TLC was programmed with both VHDL and SystemVerilog for RTL Synthesis and Post Place and Route comparison.
Design and Implementation of Dual-Axis Solar Tracker Using Microcontroller and RTC Chip.
In this project, a more efficient solar tracker is implemented based on solar energy intensity and Real time clock that helps keeping the solar panel pointed to the sun at an optimal angle all over the year. The designed system requires minimum maintenance with a practical improvement of system-efficiency at a low cost of similar output capacity.
